Key Highlights
- Real-time dashboards cut problem response time from days to minutes
- Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by up to 40%
- Data-driven forecasting improves inventory efficiency by 20-25%
- Quality analytics identify defect root causes 3x faster
- Cloud BI makes enterprise analytics affordable for small manufacturers
Why Data-Driven Manufacturing Is Essential Today
Imagine knowing tomorrow’s downtime risk today — that’s what data-driven manufacturing delivers
I’ve spent the last decade helping manufacturers make sense of their data, and I’ve noticed something: the gap between leaders and laggards keeps widening.
The factories thriving today aren’t necessarily the ones with the newest equipment—they’re the ones making better decisions faster through data-driven manufacturing.
Every production line, quality station, and warehouse scanner in your facility generates data. Most manufacturers collect this information religiously but struggle to turn it into action.
That’s where business intelligence in manufacturing industry transforms operations completely.
Business intelligence for manufacturing converts shop-floor data into real-time insights that reduce downtime by 20-40%, cut quality defects by 15%, and optimize inventory by 25%. Modern manufacturing business intelligence solutions integrate with ERP, MES, and IoT systems to deliver predictive maintenance alerts, production dashboards, and demand forecasts that transform reactive operations into proactive, data-driven manufacturing environments.
The Reality on the Factory Floor
The manufacturers I work with face similar challenges: downtime that nobody saw coming, inventory that’s either excessive or insufficient, quality issues discovered too late, and decisions based on week-old reports instead of current reality.
Business intelligence for manufacturing solves these problems by connecting your operational systems into unified dashboards that show what’s happening right now—and what you should do about it.
The importance of data-driven manufacturing becomes clear when you see results. North America represents 38% of the global BI market, with manufacturing leading adoption rates across all sectors.
The reason is simple: the ROI is measurable and often dramatic. Understanding the importance of data-driven manufacturing helps executives justify investments in advanced BI implementations.
Understanding Manufacturing Business Intelligence
Traditional manufacturing reporting looks backward. You get last week’s production numbers, last month’s quality metrics, and quarterly inventory summaries.
By the time you see problems, you’re already dealing with consequences.
Business intelligence for manufacturing shifts you from reactive to predictive. Modern manufacturing business intelligence services don’t just tell you what happened—they show you what’s happening now and help predict what’s coming next.
This fundamental shift demonstrates the importance of data-driven manufacturing in today’s competitive landscape. Business intelligence in manufacturing industry has evolved dramatically over the past decade to meet these challenges.
A Real-World Example
I worked with an automotive parts manufacturer that spent three days compiling weekly production reports in Excel.
Managers would spot efficiency drops on Friday for problems that started Monday.
After implementing advanced BI systems, those same metrics appeared on dashboards in real-time. The plant supervisor told me they now catch and fix issues the same shift they occur.
That’s the difference between looking backward and seeing forward with data-driven manufacturing.
The Four Pillars of Manufacturing BI
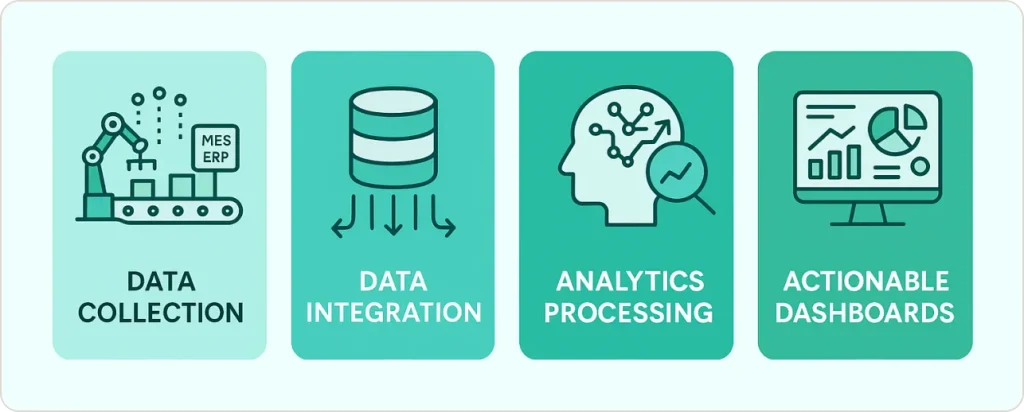
- Data Collection: Your systems work automatically—MES tracks production cycles, sensors monitor equipment health, ERP logs inventory movements, and quality platforms record inspections.
- Data Integration: Instead of scattered silos, manufacturing business intelligence solutions pull everything into a central repository—either a data warehouse or modern data lake.
- Analytics Processing: The system runs calculations, identifies trends, flags anomalies, and generates predictions using machine learning models that spot patterns humans would never catch.
- Actionable Dashboards: Plant managers see OEE trends, maintenance teams get equipment health alerts, supply chain leaders monitor inventory levels, and executives track overall operational metrics through modern BI platforms.
Why Integration Matters Most
Business intelligence for manufacturing works best when it connects seamlessly with your existing systems. The importance of data-driven manufacturing is realized through proper integration.
Modern BI platforms integrate with:
- ERP systems for financial and inventory data
- MES platforms for production tracking and work orders
- SCADA and IoT sensors for real-time equipment telemetry
- Quality management systems for inspection results
- Supply chain applications for logistics and supplier data
The manufacturers getting the best results treat integration as a first-class priority, not an afterthought.
When your BI system can correlate a quality issue with specific material batches, equipment settings, and operator shifts, you move from “what happened” to “why it happened.”
The Business Case for Business Intelligence in Manufacturing
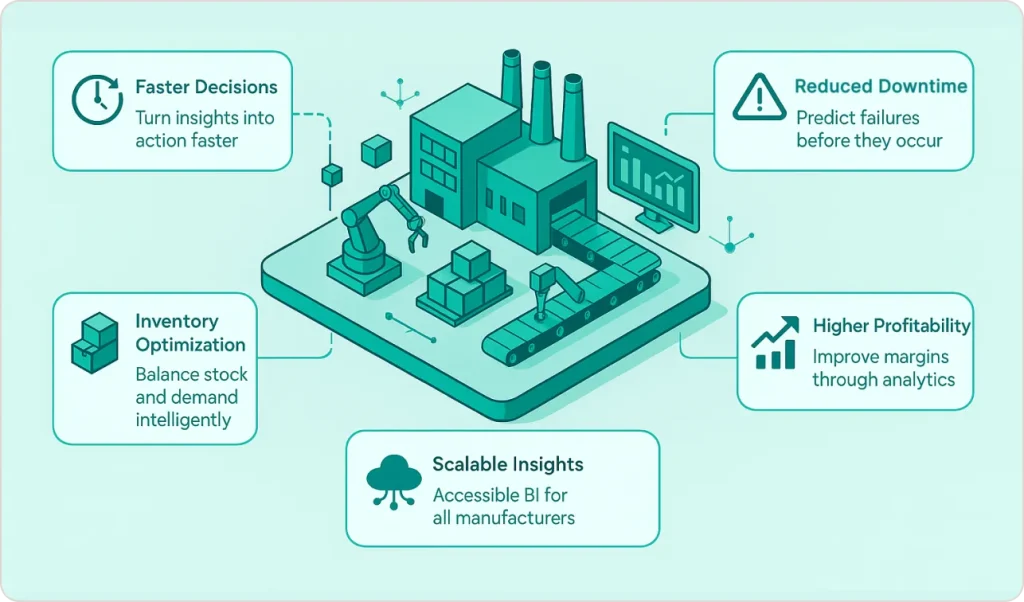
Quantifiable Benefits Across Operations
Let me share what actually happens when manufacturers implement business intelligence for manufacturing properly.
Research on data-driven digital transformation demonstrates that data-driven organizations achieve significantly higher profitability than competitors.
For manufacturers, the specific gains from manufacturing business intelligence solutions are even more compelling. This clearly illustrates the importance of data-driven manufacturing and why BI has become critical for competitive survival.
Faster Decision-Making Changes Everything
Faster decision-making emerges as the most immediate benefit. When production issues appear on dashboards within minutes instead of days, response time compresses dramatically.
A packaging manufacturer I advised reduced their problem-resolution time from 48 hours to 4 hours simply by giving supervisors real-time visibility through data-driven manufacturing.
That’s not just faster—it’s transformational. Modern BI enables this kind of operational agility.
Downtime Costs More Than You Think
Reduced downtime represents the largest financial impact for most plants implementing business intelligence for manufacturing. Unplanned equipment failures cost manufacturers thousands per hour in lost production, rush labor, and missed deliveries.
Predictive maintenance strategies can spot developing problems days or weeks before failure, allowing scheduled repairs during planned downtime windows.
Manufacturers using manufacturing business intelligence solutions for predictive maintenance report 20-40% reductions in unplanned downtime. This demonstrates the clear importance of data-driven manufacturing.
One automotive supplier I worked with calculated that every 1% reduction in downtime added $200,000 to their annual profit. That math gets executives’ attention quickly and drives BI adoption.
Inventory Optimization: The Hidden Profit Center
Inventory optimization through business intelligence in manufacturing industry delivers both cost reduction and service improvement. Companies using advanced analytics for demand forecasting balance inventory levels precisely—holding enough to meet demand without tying up excessive capital.
I’ve seen manufacturers reduce inventory investment by 20-25% while simultaneously improving service levels through data-driven manufacturing.
That’s the power of knowing what you’ll actually need rather than guessing conservatively. The importance of data-driven manufacturing shows in these tangible results.
Competitive Pressure Is Real
Your competitors are probably already using business intelligence for manufacturing. Industry surveys indicate that 62% of manufacturers now view cloud-based BI as critical to their operations.
The manufacturers still relying on manual reporting and gut-feel decisions find themselves at an increasing disadvantage. The importance of data-driven manufacturing becomes evident when comparing competitive performance.
I’ve watched this play out repeatedly. Two similar manufacturers compete for the same customers. One uses manufacturing business intelligence solutions to optimize production schedules, predict maintenance needs, and respond quickly to quality issues.
The other relies on traditional methods. Over time, the BI-enabled manufacturer offers better lead times, higher quality, and more competitive pricing—not because of better equipment, but because of better decisions through data-driven manufacturing.
SMB-Friendly Economics
Here’s what’s changed dramatically in recent years: you don’t need a Fortune 500 budget anymore for business intelligence for manufacturing.
Cloud-based manufacturing business intelligence solutions have made enterprise-grade analytics accessible to manufacturers of all sizes. Monthly subscription pricing typically starts under $1,000 for basic implementations.
Many platforms offer free tiers for initial exploration. The capital investment barrier that once kept small manufacturers from adopting advanced BI has essentially disappeared.
The strategy I recommend to smaller manufacturers: start narrow and focused. Pick your most painful problem—maybe excessive downtime on a critical machine, or quality issues with a specific product line.
Build your BI implementation around solving that one problem well. The early ROI justifies expanding to other areas, further proving the importance of data-driven manufacturing.
Critical Use Cases for Business Intelligence in Manufacturing
Production Efficiency and OEE Monitoring
Overall Equipment Effectiveness remains the definitive metric for production performance. Real-time OEE dashboards powered by business intelligence for manufacturing transform how plants operate.
Instead of calculating OEE manually at shift end, managers now see current performance continuously.
When any component of OEE drops—a machine stops unexpectedly, cycle times slow, or quality defects increase—manufacturing business intelligence solutions trigger alerts immediately.
Key benefits of OEE monitoring:
- Instant visibility into availability, performance, and quality metrics
- Automated alerts when production efficiency drops below thresholds
- Historical trend analysis to identify recurring bottlenecks
- Shift-by-shift comparison to optimize scheduling and staffing
Real-Time Visibility: Why It Changes Everything
I implemented OEE dashboards using business intelligence in manufacturing industry for a food processing plant that discovered their afternoon shift consistently underperformed.
Analysis revealed that ambient temperature affected product consistency. A relatively inexpensive climate control adjustment recovered 150 hours of productive capacity monthly.
The visibility matters most. When everyone from operators to executives sees the same real-time metrics, problems get solved faster because nobody wastes time arguing about what the numbers actually show.
Predictive Maintenance That Actually Works
Traditional maintenance follows two approaches: reactive (fix it when it breaks) or preventive (service on fixed schedules). Both waste money.
Business intelligence for manufacturing enables predictive maintenance using sensor data and analytics to identify developing problems before failure occurs.
Vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and performance tracking reveal patterns that precede equipment failures.
Predictive maintenance advantages:
- Reduce unplanned downtime by 20-40% through early problem detection
- Lower maintenance costs by replacing parts only when needed
- Extend equipment lifespan through optimized maintenance timing
- Improve production planning reliability by eliminating surprise failures
A pharmaceutical manufacturer I advised used manufacturing business intelligence solutions for predictive maintenance to monitor critical mixing equipment. The system detected abnormal vibration patterns and recommended bearing replacement during a planned weekend shutdown.
Without that warning, the bearing would have failed mid-production the following Tuesday, costing them $75,000 in downtime and emergency repairs.
Inventory and Demand Forecasting
Inventory represents a constant balancing act—hold too much and you tie up capital while risking obsolescence; hold too little and you can’t meet customer demand.
Advanced forecasting models within manufacturing business intelligence solutions analyze historical demand patterns, account for seasonality, factor in market trends, and incorporate external indicators like economic data.
Machine learning algorithms identify subtle patterns that improve forecast accuracy continuously through data-driven manufacturing.
Inventory optimization outcomes:
- 20-25% reduction in inventory carrying costs
- Improved service levels and reduced stockouts
- Better cash flow management through optimized working capital
- More efficient production scheduling aligned with actual demand
Better forecasts from business intelligence for manufacturing enable more efficient production scheduling, reduced expedited shipping and overtime costs, and more accurate workforce planning.
Quality Control and Root Cause Analysis
Quality problems are expensive on multiple levels. Rework consumes time and materials. Scrap represents pure waste. Defects reaching customers damage reputation and trigger warranty costs.
Business intelligence in manufacturing industry enables platforms to perform root cause analysis at scale.
When defect rates spike, manufacturing business intelligence solutions correlate quality data with hundreds of production variables: which shift was running, what material batches were used, equipment settings, environmental conditions, operator certifications, and maintenance history.
Quality analytics capabilities:
- Automated defect pattern recognition across production runs
- Correlation analysis linking quality issues to specific variables
- Real-time quality alerts preventing defective batch completion
- Supplier quality tracking for proactive material management
A medical device manufacturer used business intelligence for manufacturing to trace intermittent defects back to a specific supplier’s raw material. The pattern would have been impossible to spot manually—defects appeared randomly across multiple weeks and production runs.
The data-driven manufacturing system identified the common factor: one supplier’s material batch number. They quarantined remaining inventory and avoided a potential recall.
Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
Manufacturing rarely happens in isolation. You depend on suppliers for materials and components, and your customers depend on you for timely delivery.
Supply chain analytics through business intelligence in manufacturing industry provides visibility across the entire flow.
Track supplier performance metrics like on-time delivery rates, quality levels, and lead time variability.
Monitor your own delivery performance by customer, product line, and route using manufacturing business intelligence solutions.
Supply chain benefits:
- Supplier scorecards tracking on-time delivery and quality metrics
- Early warning systems for potential supply disruptions
- Transportation cost optimization through route and carrier analysis
- Customer delivery performance tracking for relationship management
When disruptions occur—a supplier ships late, a logistics provider experiences delays, or demand suddenly spikes—business intelligence for manufacturing helps you respond quickly.
The manufacturers who navigated recent supply chain disruptions most successfully were the ones who could see problems developing early and adjust plans proactively.
Implementing Business Intelligence for Manufacturing
Start With Data Foundation Assessment
Every successful implementation I’ve led started the same way: a thorough assessment of data readiness.
You need honest answers to hard questions.
Is your data accurate? I’ve seen manufacturers discover their production counts didn’t match inventory records, quality data contained gaps, and equipment sensors weren’t calibrated consistently.
Do you have data silos? Production information lives in the MES, financial data stays in the ERP, quality metrics sit in a separate QMS, and maintenance records exist in spreadsheets.
Integration challenges often exceed technical difficulty—they’re organizational and political when implementing advanced BI.
What’s your historical data quality? Manufacturing business intelligence solutions become more valuable when they can analyze trends over time. Gaps in historical data limit analytical capability.
Addressing these foundation issues before building dashboards saves enormous frustration. Visualizing bad data just makes the problems more visible without making them more solvable.
Define Clear, Measurable Objectives
I always start business intelligence for manufacturing projects by asking executives and plant managers: “What decisions will this help you make better?”
Vague goals like “improve efficiency” or “reduce costs” aren’t specific enough for data-driven manufacturing.
Effective objectives look like this:
- Reduce unplanned downtime on critical equipment by 25% within six months
- Improve first-pass yield from 91% to 95% by year-end
- Cut finished goods inventory by $750K while maintaining 98% fill rate
- Increase overall OEE from 68% to 75% across all production lines
Specific, measurable goals keep the project focused and make ROI calculation straightforward. This approach reinforces the importance of data-driven manufacturing.
Choose Appropriate Tools for Your Scale
Tool selection matters less than you’d think. The best manufacturing business intelligence solutions are the ones your team will actually use and that integrate cleanly with your existing systems.
- For smaller manufacturers: Start simple. Power BI’s free tier handles surprising complexity. Even well-designed Excel dashboards connected to your databases can deliver initial value for data-driven manufacturing.
- For mid-market manufacturers: Cloud-based business intelligence for manufacturing platforms like Power BI, Tableau, or Qlik Sense offer powerful capabilities at reasonable cost. Monthly subscription pricing makes them accessible, and cloud deployment means minimal IT infrastructure requirements.
- For large enterprises: You may need multiple specialized tools—an enterprise data warehouse, advanced analytics platforms, and manufacturing-specific applications like Siemens Opcenter or Rockwell FactoryTalk Analytics.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
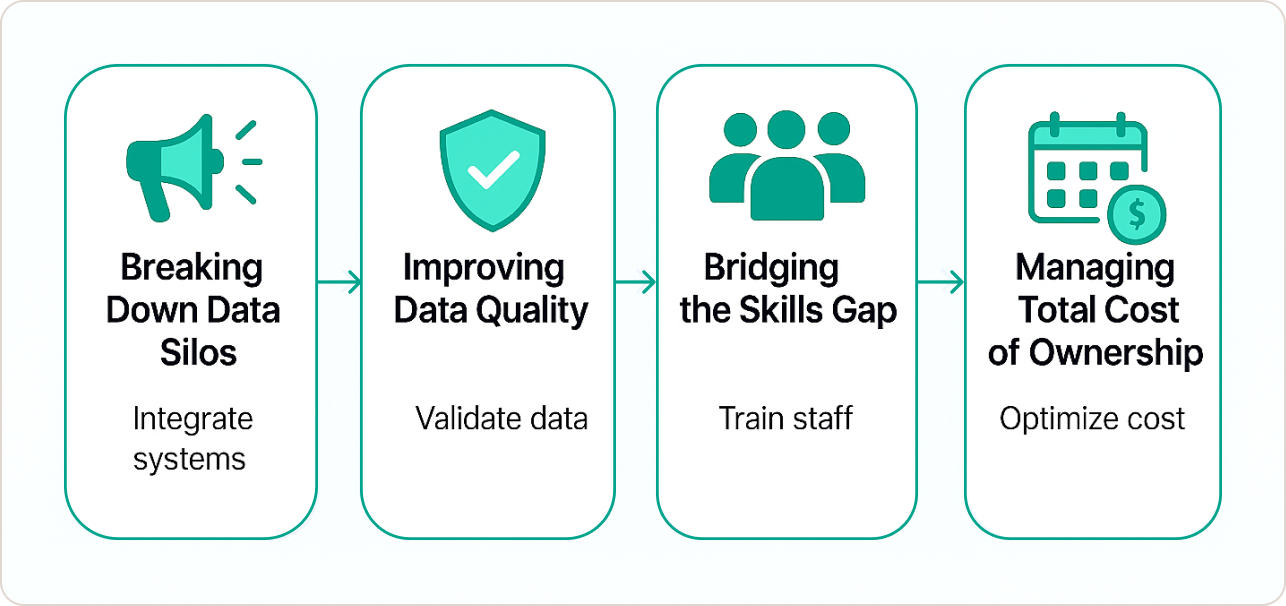
Breaking Down Data Silos
Most manufacturers have information scattered across systems that don’t communicate well.
Production data lives in the MES, financial information resides in the ERP, quality metrics exist in a separate QMS, and maintenance records hide in spreadsheets.
Solution: Implement a data integration layer—either a traditional data warehouse or modern data lake. Cloud platforms like Azure and AWS offer integration services specifically designed for manufacturing business intelligence solutions.
Sometimes custom connectors are required for legacy systems—budget for this integration work upfront rather than discovering it mid-project.
The integration challenge is often more organizational than technical. Different departments control different systems and may resist sharing data.
Executive sponsorship helps overcome these political obstacles in data-driven manufacturing initiatives.
Improving Data Quality
Garbage in, garbage out. If source data is inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent, business intelligence for manufacturing insights won’t be reliable.
Solution: Implement data quality processes before building dashboards:
- Standardize naming conventions and measurement units
- Establish validation rules that catch errors at entry
- Clean historical data systematically
- Assign data stewards responsible for quality in each operational area
Start measuring data quality itself as a KPI for your manufacturing data analytics solutions. Track error rates, completeness percentages, and timeliness metrics.
What gets measured improves in data-driven manufacturing. Understanding the importance of data-driven manufacturing includes prioritizing data quality across all BI implementations.
Bridging the Skills Gap
Plant managers understand manufacturing but may not be comfortable with analytics tools. IT teams know databases but might not grasp production operations.
Solution: Bridge the gap through training and strategic hiring:
- Provide structured training programs for existing staff
- Start with intuitive, self-service business intelligence for manufacturing tools
- Build a center of excellence to support analytics across the organization
Don’t assume people will figure out BI independently. Capability development requires investment in data-driven manufacturing.
Managing Total Cost of Ownership
Implementing manufacturing business intelligence solutions can become expensive—software licenses, infrastructure, integration work, training, ongoing support.
Solution: Control costs strategically:
- Use cloud-based business intelligence for manufacturing to eliminate infrastructure expenses
- Start with single use cases and expand incrementally
- Leverage free or low-cost tools for initial pilots
- Calculate ROI clearly to justify investment in expansion
For smaller manufacturers, subscription-based data-driven manufacturing platforms offer enterprise capabilities without enterprise budgets.
Ready to Transform Your Operations?
After working with manufacturers for over a decade, I’ve learned this: the companies thriving today aren’t necessarily the ones with the newest equipment—they’re the ones making better decisions faster through business intelligence for manufacturing.
Data-driven manufacturing isn’t optional anymore. Customer expectations rise continuously, margins tighten, and competition intensifies. The importance of data-driven manufacturing is clear in today’s competitive landscape.
The manufacturers winning are the ones using manufacturing business intelligence solutions to find hidden efficiencies, predict problems before they occur, and optimize operations systematically.














