TL;DR
- Your analysts waste 50-70% of their time on data prep. Generative AI automates ETL pipelines, query writing, and data cleaning, cutting preparation time by half.
- ROI is proven: Organizations with structured governance achieve 347% median ROI, while 95% of ungoverned pilots fail.
- Start with metadata: 67% of companies lack data trust. Fix your data documentation and lineage before deploying AI, or you’ll amplify existing problems.
Why Your Analytics Team Needs Generative AI (And Why Most Implementations Fail)
I’m going to tell you something uncomfortable: if your data team spends more than half its time cleaning data and writing queries instead of generating insights, you’re not competing in 2025.
Here’s what I see across the 70+ analytics practices I’ve worked with: talented analysts buried under ticket backlogs, CDOs frustrated by slow time-to-insight, and expensive BI tools sitting at 26% user adoption because they’re too complex for business stakeholders.
Generative AI for data analytics solves this, but only if you implement it correctly.
According to McKinsey’s 2025 Global Survey, 72% of U.S. organizations now use AI in some capacity, with 65% deploying generative AI regularly in at least one business function. That’s nearly double the adoption rate from just ten months earlier.
But here’s the disconnect: 67% of those same organizations don’t trust their data quality. They’re racing to implement AI on top of a broken data infrastructure. That’s why 95% of generative AI pilots never make it to production.
The difference between companies achieving 347% ROI and those watching pilots fail? They fixed their metadata and governance first.
Unlike traditional BI tools that require SQL expertise and manual chart-building, generative AI lets business users ask questions in plain English and automatically generates queries, visualizations, and insights in seconds.
Quick Answer
Generative AI creates SQL queries, visualizations, and synthetic datasets from natural language prompts, automating analytics tasks that previously required manual coding and reducing analyst workload by 50-70%.
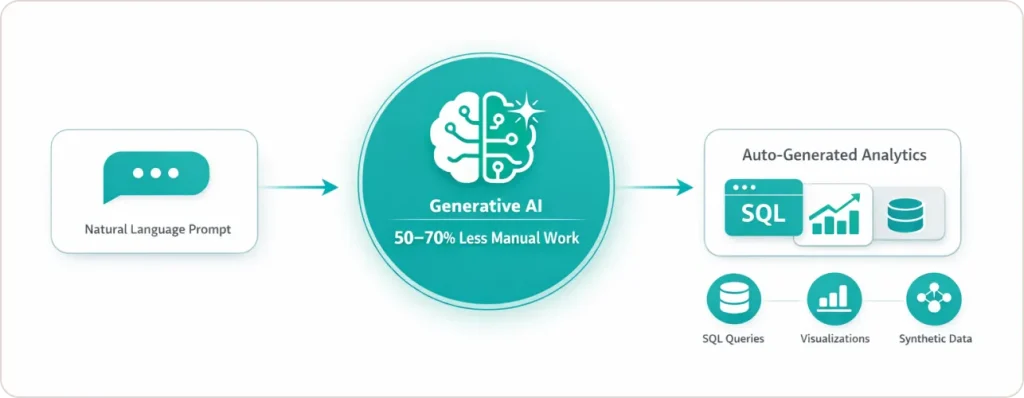
The 8 Use Cases for Generative AI That Deliver Measurable ROI
1. How Does Generative AI Automate ETL and Data Pipelines?
Generative AI writes ETL code, schedules pipeline jobs, and monitors data flows automatically, reducing engineering time by 50-70%.
Last year, I worked with a retail analytics team drowning in 40+ data integration requests. Their two data engineers couldn’t keep up. We implemented an LLM-based ETL generator where business analysts described their data needs in plain English: “Pull yesterday’s sales from Snowflake, join with inventory levels, flag any stockouts, and load to our warehouse.”
The AI generated complete dbt models, tested them, and scheduled the jobs. Within six weeks, they cleared the backlog. The engineers shifted focus to data quality monitoring and semantic layer design—work that actually required human judgment.
Real technical architecture:
- Daily sales data lands in BigQuery
- Vertex AI models analyze patterns and predict demand
- Looker auto-generates dashboards with stock recommendations
- AI agents monitor the pipeline, alerting on failures and recommending optimizations
If your data engineering team is spending more time on pipeline maintenance than solving new business problems, our data engineering services can help you implement AI-assisted pipelines that reduce technical debt.
2. Why Synthetic Data Generation Matters (And When to Use It)
Synthetic data generation creates realistic datasets that preserve statistical properties while protecting privacy, enabling model training and testing in regulated industries.
A healthcare AI project I advised had only 200 MRI scans of a rare disease—not enough to train a diagnostic model. Using generative adversarial networks, they created 2,000 synthetic MRI scans that maintained the same anatomical patterns and statistical distributions as real scans, but contained zero patient information. Model accuracy improved 40%, and they stayed HIPAA-compliant.
According to industry research, 63% of organizations now use synthetic data for at least some model training.
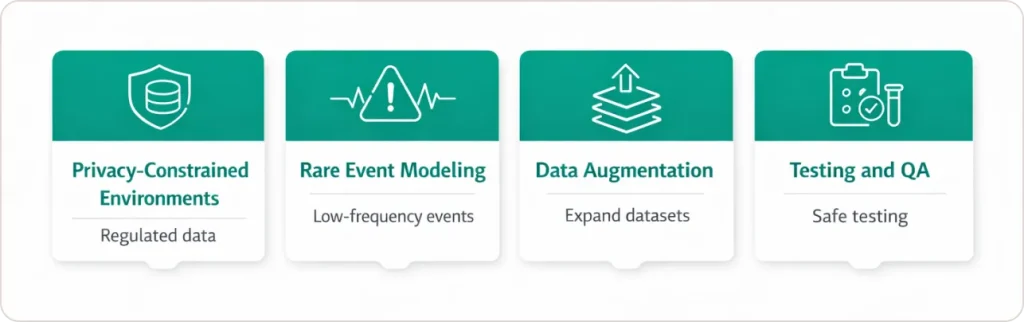
Where synthetic data delivers value:
- Privacy-constrained environments: Healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI-DSS), government (classified data)
- Rare event modeling: Fraud detection, equipment failure prediction, disease diagnosis
- Data augmentation: Balancing imbalanced datasets, expanding limited training sets
- Testing and QA: Creating realistic test data for analytics applications without production data exposure
Critical limitation: Synthetic data works for pattern recognition but not for use cases requiring absolute data fidelity, like forensic accounting or legal discovery.
3. How Natural Language Interfaces Democratize Analytics
Natural language interfaces let business users query data through conversational prompts instead of SQL, increasing analytics adoption from 26% to a potential 10x improvement.
Traditional BI penetration is stuck at 26-30% because tools are too complex. A marketing director shouldn’t need six months of training to answer “Which campaigns drove the most revenue last quarter?”
With conversational BI powered by generative AI, they ask that question in Slack. The system:
- Interprets the intent (“revenue attribution by campaign”)
- Generates the appropriate SQL query
- Executes against the data warehouse
- Creates visualizations
- Writes a natural language summary
- Suggests three follow-up analyses
All in under 10 seconds.
Real implementation at a SaaS company: Their customer success team used to file 15-20 data requests per week with the analytics team, waiting 2-3 days for responses. We deployed a natural language interface (similar to Power BI Copilot) trained on their semantic model. Within two months:
- Data requests to analysts dropped 60%
- CS team satisfaction with data access jumped from 3/10 to 8/10
- Average time from question to answer went from 2 days to 2 minutes
Critical Implementation Warning
Your AI is only as good as your metadata. If your data catalog has inconsistent naming conventions, missing documentation, or unclear business definitions, your AI will generate wrong answers confidently.
Before implementing natural language analytics, you need:
- Semantic layer: Business-friendly definitions mapped to technical tables
- Data lineage: Clear understanding of where data comes from
- Validation rules: Automated checks that catch nonsensical queries
If you’re still documenting data manually in spreadsheets, read the blog that discusses how data governance roles and responsibilities can help you build the metadata infrastructure that makes AI-powered analytics reliable.
4. AI-Generated Visualizations: Beyond Auto-Charting to Narrative Intelligence
Generative AI creates context-aware visualizations and writes analytical narratives automatically, transforming raw data into presentation-ready insights in seconds rather than hours.
This isn’t just about auto-generating bar charts. It’s about narrative intelligence.
A Fortune 500 client used to spend four hours every Monday compiling executive KPI reports. Pulling data from six systems, building charts in PowerPoint, and writing summaries. We implemented an AI-generated reporting workflow where the system:
- Queries all data sources automatically
- Identifies significant changes (not just “what happened” but “what’s different”)
- Generates appropriate visualizations based on data type and relationships
- Writes narrative summaries highlighting key insights
- Flags anomalies requiring human attention
Now their Monday morning report generates automatically at 6 AM. The analyst’s role shifted from report assembly to report validation and strategic interpretation.
Example AI-generated narrative:
“Q4 revenue increased 5% to $47.3M, driven primarily by Northeast region performance (+12%) and enterprise segment growth (+$2.1M). However, SMB customer churn rose 3.2 percentage points to 8.7%, concentrated in the <$50K ARR segment. Recommend a targeted retention campaign for at-risk accounts identified in the dashboard.”
The AI doesn’t just state facts. It connects patterns, identifies exceptions, and suggests next steps.
5. Predictive Analytics and Scenario Modeling: From Forecasts to Futures
Generative AI simulates thousands of “what-if” scenarios by creating synthetic future states based on historical patterns and hypothetical inputs, enabling proactive strategy testing without waiting for real-world data.
Traditional forecasting shows you one predicted future based on trend lines. Generative AI shows you 500 possible futures based on different assumptions.
A regional retailer I worked with used generative scenario modeling to prepare for demand volatility. They prompted the system: “Model inventory needs under three scenarios: normal holiday season, 15% recession impact, and supply chain disruption lasting 90 days.”
The AI generated:
- Demand projections for each scenario
- Cash flow implications
- Recommended inventory levels by product category
- Supplier diversification strategies
They ran this in the afternoon. Their previous scenario planning process took the finance team three weeks and covered only two scenarios.
Where this delivers strategic value:
- Supply chain planning: Stress-testing logistics under disruption scenarios
- Financial modeling: Revenue projections across economic conditions
- Risk assessment: Simulating regulatory changes or competitive moves
- Capacity planning: Forecasting infrastructure needs across growth scenarios

Critical nuance: Generative AI scenario modeling works best for bounded uncertainty (known variables, unknown values) rather than black swan events (unknown unknowns). If you’re modeling COVID-2.0 scenarios, the AI has no historical pattern to learn from.
6. Fraud Detection and Anomaly Detection: Pattern Recognition at Scale
Generative AI improves anomaly detection by learning normal behavior patterns with higher precision than rule-based systems, then identifies deviations while reducing false positives by up to 50%.
The gold standard example: Mastercard deployed generative AI for fraud detection and achieved:
- 2x improvement in fraud detection rates
- 300% faster merchant identification
- 200% reduction in false positives
Here’s why generative AI works better than traditional rules engines: Instead of defining “fraud is a transaction over $5,000 from a new location,” the AI learns normal patterns for each customer. Purchase frequency, typical merchants, geographic patterns, and time-of-day preferences. Then, flag deviations with probabilistic scoring.
When a transaction trips the threshold, the system explains why:
“This transaction is flagged because: (1) purchase location is 500 miles from last activity 2 hours ago (geographically impossible), (2) merchant category (luxury goods) inconsistent with 12-month purchase history (groceries, gas), (3) transaction size ($3,200) exceeds 95th percentile of normal behavior ($180).”
That explainability builds trust with fraud investigators and reduces alert fatigue.
7. Code Generation and Legacy Migration: Accelerating Development by 60%
Generative AI writes SQL queries, Python scripts, and transformation logic from natural language, reducing development time by 40-60% and enabling rapid migration of legacy analytics code to modern platforms.
One of my best client success stories: They needed to migrate 200+ Qlik dashboards to Power BI. Manual conversion estimate: 18 months with two full-time developers.
We used an LLM trained on Qlik Sense expressions and Power BI DAX to auto-convert the calculation logic. Timeline dropped to four months. The AI handled about 80% of conversions automatically. The remaining 20% required manual adjustments for complex calculations and custom functions.
Code Generation Risks You Can’t Ignore: AI-generated queries might work functionally but have catastrophic performance issues. Never deploy AI-generated code without human code review, automated testing, and query plan analysis for efficiency.
8. Personalized Analytics: From Segment Reports to Individual Insights
Generative AI analyzes individual behavior patterns to create tailored insights and recommendations, moving beyond generic segment reporting to true 1:1 personalization at scale.
A B2B SaaS company I worked with had a problem: their customer success team was manually reviewing account health data for 800+ customers, trying to identify churn risks. The process was inconsistent. Some CSMs were great at pattern recognition, others missed obvious signals.
We implemented a generative AI system that:
- Analyzed each account’s product usage, support ticket patterns, payment history, and engagement metrics
- Generated personalized health scores with specific risk factors
- Recommended next-best-actions tailored to each account’s situation
- Created customized email templates for outreach
Result: Churn dropped 18% in the first quarter after implementation.
“Generative AI excels at turning unstructured data into structured insights, but data must be in excellent shape with human validation for reliability.” — Thomas H. Davenport, Babson College
What Challenges Does Generative AI Face with Respect to Data?
Let me be direct: The biggest barrier to generative AI success isn’t the AI. It’s your data infrastructure.
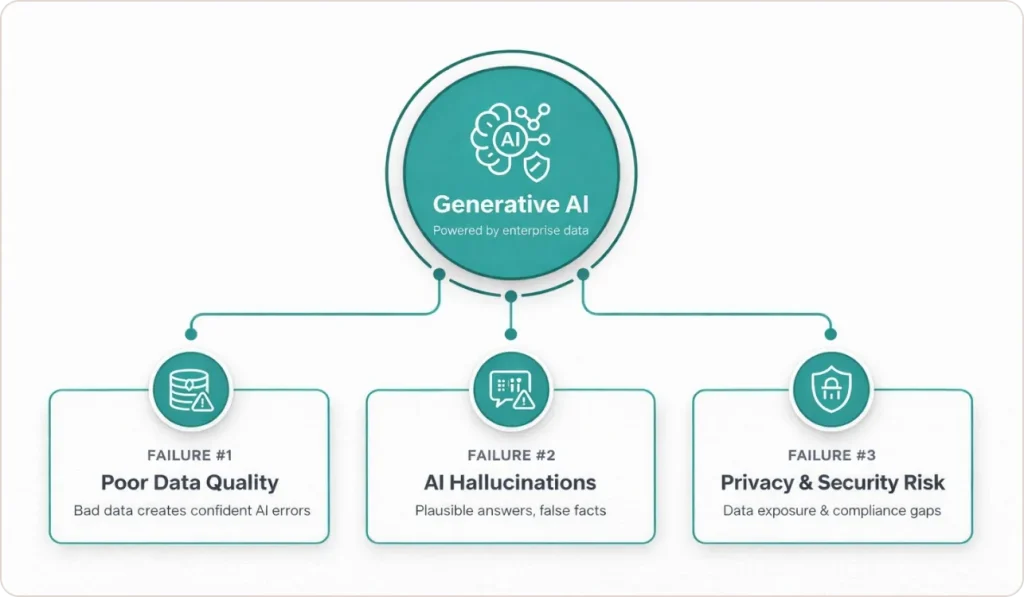
Challenge #1: Data Quality Amplifies Problems
The problem: 67% of organizations lack confidence in their data quality. When you feed flawed data into generative AI, you don’t get flawed insights. You get confidently wrong insights delivered at scale.
I worked with a financial services firm that deployed AI-powered customer analytics. The AI started recommending high-risk loans because it learned from historical data containing data entry errors—loan amounts stored in the wrong currency field.
What this actually costs:
- Decisions made on incorrect AI outputs
- Lost trust when stakeholders catch AI errors
- Rework costs (fixing data after problems emerge)
The fix:
- Implement automated data quality monitoring (tools like Great Expectations, Soda, or dbt tests)
- Establish data quality SLAs before AI deployment
- Run AI outputs parallel to manual processes for 4-8 weeks to validate accuracy
Challenge #2: AI Hallucinations Generate Plausible Nonsense
The problem: Large language models can generate outputs that sound correct but are factually wrong. Inventing metrics, misinterpreting relationships, or creating trends that don’t exist in your data.
Example: A marketing team asked their AI tool, “What was our ROI on the Q3 email campaign?” The AI confidently replied, “327% ROI based on $45K spend and $147K attributed revenue.” Problem: They didn’t run an email campaign in Q3.
The fix: Human-in-the-Loop Validation: BCG’s analysis of 350+ GenAI projects shows structured approaches with human oversight in early stages yield 10-15x ROI within 3 years, versus scattered pilots with minimal impact.” — BCG, Stairway to GenAI Impact
Challenge #3: Data Privacy and Security Risks
Using third-party LLM APIs means your data leaves your environment. For regulated industries, this creates compliance violations.
The fix:
- Use private deployments (Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, self-hosted models)
- Anonymize data before feeding it to AI systems
- Ensure vendor agreements prohibit data retention and model training
Platform Comparison: Which Tool Fits Your Stack?
| Platform | Best For | Pricing | Setup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snowflake Cortex | Teams on Snowflake | $$$ | Medium |
| Databricks AI/BI | Data science teams | $$$ | Medium-High |
| Google Vertex AI + BigQuery | Google Cloud customers | $$ | Medium |
| Microsoft Fabric Copilot | Power BI enterprises | $$ | Low |
| AWS Bedrock + Athena | Regulated industries | $$$$ | High |
| Power BI Copilot | Excel-heavy teams | $ | Very Low |
Key takeaway: Unless you have unique compliance requirements (government-classified data, proprietary algorithms), vendor platforms deliver faster ROI than custom builds. Start with embedded AI in tools your team already uses.
If you’re evaluating which platform fits your architecture, our data analytics consulting can help you assess options based on your existing tech stack and compliance requirements.
The Bottom Line: Start Small, But Start Now
Here’s what I tell every client: Generative AI for data analytics isn’t a future trend. Your competitors are already using it. The question isn’t “should we implement AI?” It’s “how do we implement it without wasting six months on a failed pilot?”
The organizations winning right now aren’t the ones with the fanciest AI models. They’re the ones who:
- Fixed their data foundation first (metadata, governance, quality monitoring)
- Started with a low-risk, high-impact pilot (automated reporting, not financial forecasting)
- Implemented human-in-the-loop validation (trust through consistency, not promises)
95% of generative AI initiatives fail because organizations skip step 1 and rush to deployment.
Don’t be part of that statistic.
The window for competitive advantage is narrowing. By 2027, AI-augmented analytics will be table stakes, not a differentiator. The advantage goes to organizations that implement thoughtfully now, not those who wait until it’s required.














