Key Highlights
- Configure GA4 to exclude all PHI-containing URL parameters automatically
- Implement server-side tagging for ultimate data control and protection
- Set minimum data retention periods and enable User Deletion APIs
- Deploy consent management integrated with Google’s Consent Mode v2
- Establish monthly audit protocols using BigQuery exports for PHI detection
Quick Compliance Check: Are You at Risk?
☐ GA4 tracking is active on your patient portal
☐ Your appointment URLs contain names, DOB, or medical info
☐ You’re tracking form submissions with symptom data
☐ You haven’t excluded PHI-containing URL parameters
If you checked ANY box, you’re potentially violating HIPAA right now. Last year, a prominent hospital system paid $4.75 million to settle a lawsuit—all because of a misconfigured Google Analytics tag. The violating code? Seven lines. The setup time? Fifteen minutes. The cost? $317,000 per minute of implementation.
As someone who’s spent over 15 years implementing analytics across healthcare organizations, I’ve witnessed how the promise of data-driven patient acquisition collides with HIPAA compliance reality. The Office for Civil Rights issued explicit guidance in December 2022 warning that tracking technologies can violate HIPAA when they collect identifiable health information.
This guide provides a battle-tested, step-by-step framework to implement GA4 without becoming the next compliance headline.
The Core Problem: Why GA4 + Healthcare = Risk
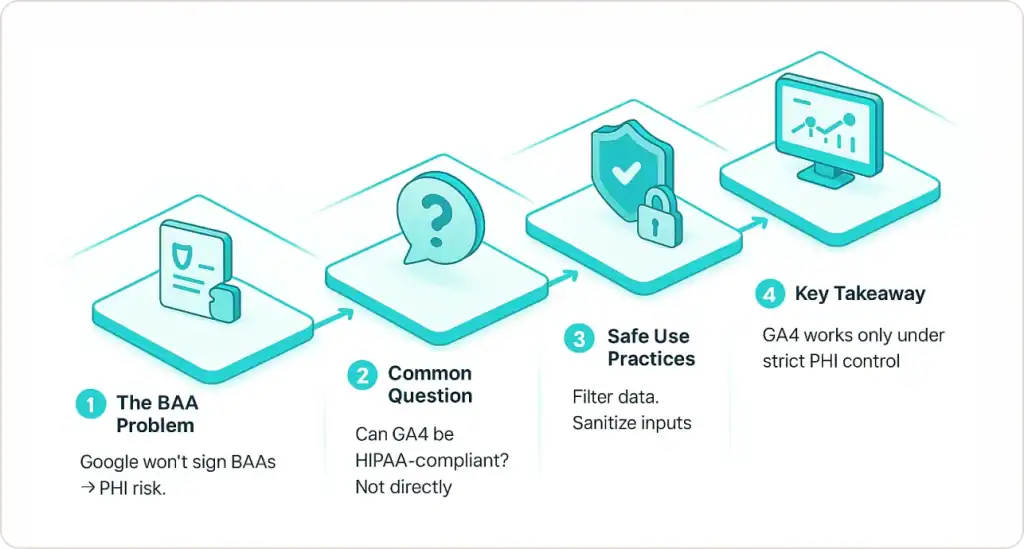
The Google Analytics BAA Problem
Here's the fundamental challenge: HIPAA requires covered entities to obtain a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) from any vendor handling PHI. Google explicitly states they do not sign BAAs for Google Analytics—making any PHI transmission a HIPAA violation.
💡 Common Question: Can Google Analytics 4 ever be fully HIPAA-compliant?
Answer: No. Google doesn't sign Business Associate Agreements for GA4. However, you can use it compliantly by preventing all Protected Health Information from reaching Google's servers through proper configuration.
Explanation: The tool itself isn't compliant, but your usage of it can be. This requires architecting your implementation to guarantee zero PHI transmission—treating GA4 as a tool that operates only on de-identified, aggregated data. The responsibility falls entirely on your organization to prevent PHI from ever reaching Google's servers through careful configuration and ongoing monitoring.
What Counts as PHI in Web Analytics?
Protected Health Information isn't just medical records. HIPAA defines 18 identifiers that, when combined with health context, become PHI:
Common PHI Scenarios That Break Compliance:
- ❌ yoursite.com/confirm?appointmentID=12345&patientName=Smith
- ❌ Form submissions capturing "reason for visit" or symptoms
- ❌ IP addresses + timestamps from oncology department pages
- ❌ Search queries like "cardiologist for chest pain treatment"
Recent Enforcement Reality: By mid-2023, multiple healthcare systems faced investigations after researchers demonstrated that common tracking pixels transmitted patient-identifiable information. The FTC has taken enforcement action against companies for sharing sensitive health data, and HIPAA penalties range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with annual caps of $1.5 million per violation category.
The 9-Step HIPAA Compliance Checklist for GA4
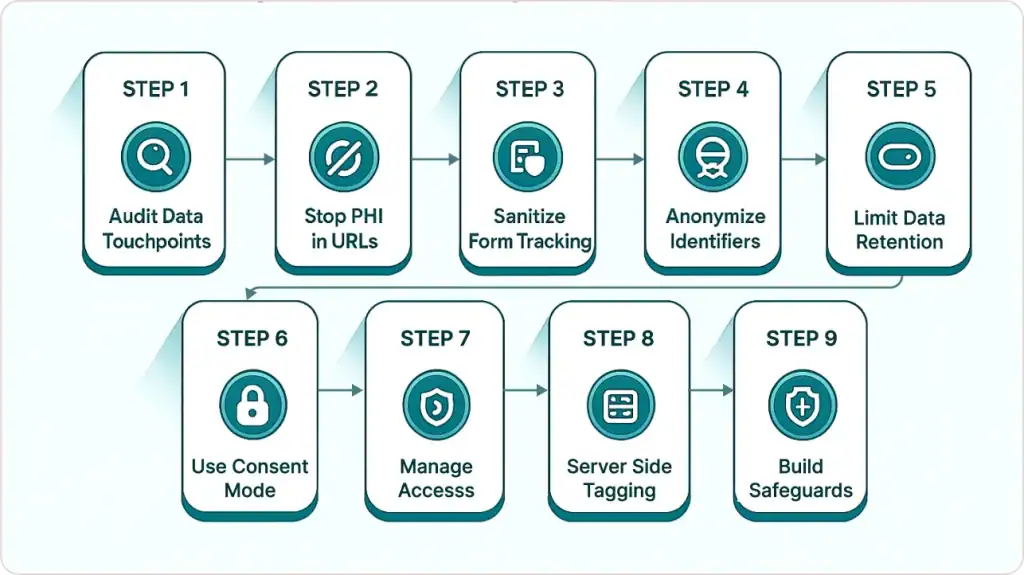
Step 1: Audit Your Data Touchpoints (30 Minutes)
Before touching GA4 settings, identify every PHI risk point:
Create a simple spreadsheet mapping:
- All website forms and field types
- URL structures with dynamic parameters
- Patient portal boundaries
- Third-party embedded tools (chat widgets, schedulers)
Pro Tip: Use browser developer tools to audit all network requests on sensitive pages. Patient portals often load third-party resources that trigger GA4 events even when you've removed primary tracking code.
Step 2: Stop Patient Data Leaking Through URLs (5-Minute Fix)
GA4 automatically captures full URLs including query parameters. If your appointment confirmation URL contains names or dates, you're sending PHI to Google.
Implementation Steps:
- Navigate to Admin > Data Streams > [Select stream]
- Click Configure tag settings > Show more
- Under "List unwanted referrals", add these parameters:
name, firstname, lastname, patientname, email, phone, mobile, dob,
birthdate, dateofbirth, ssn, appointmentid, patientid,
medicalrecordnumber, condition, symptoms, diagnosis, insuranceid
This strips specified parameters before GA4 processes them.
⚠️ CRITICAL: Parameter exclusion is reactive protection. Better practice: redesign URLs to never include PHI. Use session-based identifiers or POST requests instead of GET parameters.
Step 3: Sanitize Form Tracking Without Losing Conversions
Track form submission events (yes/no), never field contents.
Safe GA4 Event Structure:
gtag('event', 'form_submission', );
If using Google Tag Manager: Configure form triggers with "Don't capture form fields" selected. For critical forms collecting health information, implement server-side validation—your server sends sanitized events to GA4 containing only aggregated metadata.
Step 4: Anonymize User Identifiers Correctly
GA4's IP Anonymization: Enabled by default (improvement over Universal Analytics), but that's only one of 18 HIPAA identifiers.
User-ID Feature Warning: Never use patient medical record numbers, email addresses, or any identifier appearing in your patient database. If you must use User-ID for authenticated general health content areas, generate a one-way cryptographic hash:
const hashedID = await crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-256',
new TextEncoder().encode(userEmail + 'secure-salt-string'));
Safer approach for most healthcare implementations: Don't use User-ID at all.
Step 5: Configure Minimum Data Retention
Recommended Settings:
- Navigate to Admin > Data Settings > Data Retention
- Set to "2 months" (minimum available)
- Set "Reset user data on new activity" to OFF
Shorter retention limits PHI exposure if misconfigured data slips through. This impacts historical reporting—balance compliance with analytics needs by exporting critical data to BigQuery with additional security controls.
Implement Data Deletion: GA4's User Deletion API should be part of your HIPAA breach response plan if PHI is accidentally collected.
Step 6: Deploy Consent Management with Google Consent Mode
While user consent doesn't exempt you from HIPAA, implementing proper consent management demonstrates good-faith privacy efforts:
Implementation:
// Default to denied before consent
gtag('consent', 'default', );
// Update when users accept
gtag('consent', 'update', );
Integrate with platforms like OneTrust or Cookiebot, and ensure your privacy policy explicitly describes analytics usage.
Critical Point: Consent Management supplements PHI prevention—it doesn't replace it. Even with consent, you cannot track PHI in GA4.
Step 7: Establish Access Controls (15 Minutes)
HIPAA requires the "minimum necessary" principle:
GA4 Access Management:
- Assign roles (Viewer, Analyst, Editor, Administrator) based on genuine need
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all users
- Conduct quarterly access reviews to remove departed staff
- Create separate properties for different business units
Documentation Requirement: Maintain a spreadsheet listing all GA4 users, their roles, business justification, and access review dates for HIPAA audit readiness.
Step 8: Server-Side Tagging for Maximum Control (Advanced)
For organizations needing ultimate control, server-side Google Tag Manager proxies analytics through your infrastructure:
How It Works:
- Browser sends data to your server endpoint (not directly to Google)
- Server-side GTM container processes requests
- Server applies PHI scrubbing rules (regex filtering, parameter stripping)
- Only sanitized data forwards to GA4
Benefits: Complete visibility, server-level filtering, enhanced security, reduced client-side JavaScript.
Investment Required: Google Cloud infrastructure adds $100-500/month depending on traffic. Best suited for larger healthcare systems.
Step 9: Create Organizational Safeguards
Essential Controls:
Quarterly Training: Cover what constitutes PHI in digital contexts, GA4 risks, incident reporting, and real breach examples.
Change Management: Require compliance review before analytics changes: Marketing proposes → Analytics reviews for PHI risk → Compliance approves → Implementation.
Monthly Audits:
- Export raw event data via BigQuery
- Run regex scans for email patterns: \b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]\b
- Review new custom dimensions/events
- Validate parameter exclusions remain configured
Incident Response Plan: Document procedures if PHI is discovered—immediate data collection halt, User Deletion API usage, OCR reporting if thresholds met, root cause analysis.
“We Almost Made Headlines”: Real Implementation Case Study
Sarah, marketing director at a 300-bed community hospital, discovered their GA4 implementation during a routine compliance audit. Patient names appeared in analytics URL reports.
“I felt sick,” Sarah recalls. “We’d been tracking PHI for eight months without knowing it.”
The Smoking Gun:
- Appointment confirmation pages passed ?patientName= and ?phone= parameters
- Approximately 12,000 patient records potentially compromised
- 48-hour timeline to implement emergency fixes
Our Implementation:
- Week 1-2: Complete data inventory across 2,000+ pages
- Week 3-4: GA4 property rebuild with all compliance configurations
- Week 5-6: GTM restructuring, complete patient portal tracking removal
- Week 7-8: URL architecture redesign with development team
Results After 6 Months:
✅ Zero PHI incidents in monthly audits
✅ 23% increase in appointment requests from optimized campaigns
✅ Passed external HIPAA audit with no analytics findings
✅ Hospital counsel approved expanded GA4 usage
Key Success Factor: The CMO and CISO jointly sponsored the project, ensuring both marketing objectives and compliance requirements received equal priority.
At SR Analytics, we’ve helped dozens of healthcare organizations achieve this balance through our specialized Healthcare Data Analytics consulting.
Advanced HIPAA-Compliant Techniques
Cross-Domain Tracking Without PHI Leakage
Healthcare systems often operate multiple domains. Safe implementation requires:
- Configure cross-domain measurement: Admin > Data Streams > Configure your domains
- Add all related domains to cross-domain list
- Critical: Ensure linker parameter (_gl=) doesn’t appear on PHI-containing URLs
- For authenticated transitions, use server-side session management
Attribution Modeling for Healthcare Marketing
HIPAA-compliant attribution requires privacy-preserving techniques:
- Focus on campaign-level and channel-level performance (not individual journeys)
- Use GA4’s data-driven attribution (operates on aggregated patterns)
- Implement UTM parameters consistently
- Accept that some attribution granularity is sacrificed for compliance
You’ll understand: “Our cardiology campaign drove 50 appointments” without tracking specific individuals.
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Pitfall 1: “We’ll just exclude the patient portal”
Reality: PHI exists on public pages—appointment forms, symptom checkers, provider search with conditions.
Pitfall 2: “IP anonymization solves HIPAA”
Reality: That’s one of 18 identifiers. Email in URL parameters remains PHI with anonymized IP.
Pitfall 3: “Our consent banner makes this legal”
Reality: User consent is irrelevant to HIPAA. Covered entities cannot obtain “consent” to mishandle PHI.
Pitfall 4: “We’ll fix compliance later”
Reality: Once PHI enters GA4, it’s on Google’s servers permanently beyond your control.
Your Implementation Roadmap
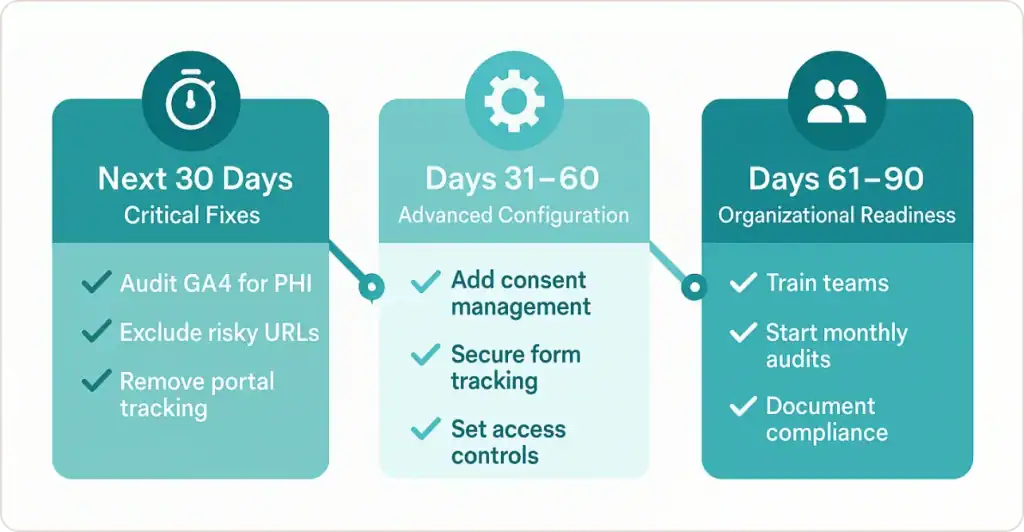
Next 30 Days (Critical Fixes)
- ✅ Audit current GA4 for PHI using this checklist
- ✅ Implement URL parameter exclusion
- ✅ Remove tracking from patient portals
Days 31-60 (Advanced Configuration)
- ✅ Deploy consent management
- ✅ Set up form tracking safeguards
- ✅ Establish access controls
Days 61-90 (Organizational Readiness)
- ✅ Train your marketing and IT teams
- ✅ Create monthly audit protocols
- ✅ Document all compliance measures
Conclusion: Compliance as Competitive Advantage
Healthcare organizations that implement truly compliant analytics gain strategic advantages: patient trust through demonstrated data protection commitment, risk mitigation avoiding costly violations, better data quality through disciplined collection practices, and organizational capability building cross-functional expertise.
Google Analytics 4 offers powerful capabilities for understanding patient behaviors and measuring marketing effectiveness. You don’t choose between analytics and compliance—you architect analytics with compliance as a core requirement from day one.
Can’t wait 90 days to implement this? Our team at SR Analytics has deployed HIPAA-compliant GA4 for 50+ healthcare organizations—completing in 2 weeks what takes most teams 3 months. We bridge the gap between complex technical requirements and business objectives, implementing analytics that deliver insights while maintaining bulletproof compliance.
Ready to implement GA4 without HIPAA risk? Explore how our specialized Healthcare Data Analytics expertise can accelerate your compliant analytics journey—turning regulatory requirements into competitive advantages that build sustainable, trust-based patient relationships.














