Key Highlights
- Cognitive mapping and F-pattern reading boost dashboard adoption rates by 60% over traditional layouts
- Data type optimization cuts enterprise Power BI dashboard load times by up to 70%
- AI-powered Smart Narrative and Copilot represent 2025’s cutting-edge dashboard storytelling capabilities
- Strategic color psychology improves comprehension while meeting WCAG 2.1 accessibility standards
- Governance frameworks with testing protocols ensure successful enterprise dashboard scaling
- Advanced DAX and custom visual techniques unlock hidden Power BI capabilities most consultants miss
73% of business dashboards are opened once and never used again—here’s how to build Power BI dashboards that actually drive decisions.
Your team spent weeks building the perfect Power BI dashboard. Charts are aligned, colors match your brand, and every KPI you could think of is displayed beautifully. Then you present it to leadership—and watch them glance at it for 30 seconds before asking, “What does this actually mean for our business?”
The problem isn’t your data or technical skills—it’s that most Power BI dashboard design focuses on what looks good rather than what drives decisions. In 15 years of consulting, I’ve discovered that dashboards succeed based on human psychology, not technical features.
This guide reveals the frameworks that turn pretty visualizations into business-critical tools, covering cognitive processing patterns, performance optimization, and specific Power BI design techniques that consistently deliver measurable results.
Power BI dashboard design success depends on audience-centric Power BI layouts, cognitive processing patterns, and performance optimization rather than visual complexity. Strategic Power BI dashboard examples outperform feature-heavy approaches.
The 7 Core Principles of Effective Power BI Dashboard Design
1. Master Audience-Centric Dashboard Design
The most common mistake I see in Power BI dashboard design isn’t technical—it’s human psychology. You’re designing for yourself, not your audience. I once spent three weeks perfecting a dashboard with every metric imaginable, only to watch the VP glance at it for five seconds and ask, “What am I supposed to do with this?”
Understanding Mental Models in Power BI Design
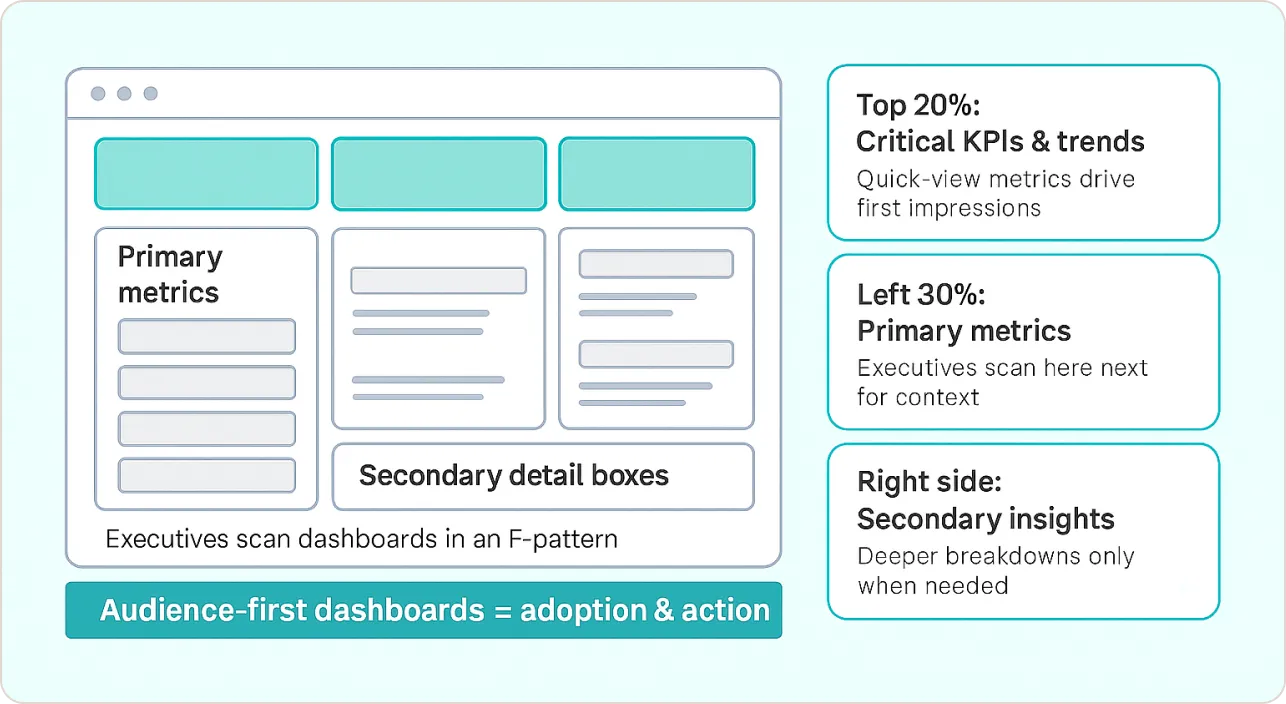
Different roles process Power BI visualization differently. When I designed Power BI dashboard examples for a healthcare network’s executive team, I discovered they scan information in an F-pattern, focusing on top-left quadrants first. This led me to develop what I call the “Executive Power BI Dashboard Design Framework”:
- Top 20%: Critical KPIs and trend indicators
- Left 30%: Primary metrics with clear variance indicators
- Center: Supporting context and drill-down capabilities
- Right side: Secondary insights and detailed breakdowns
Practical Power BI Layout Implementation
For each Power BI dashboard design, I conduct stakeholder interviews using these questions:
- What decisions does this Power BI visualization need to support?
- How often will you reference these Power BI dashboard examples?
- What context do you need to trust the numbers?
- When would you want to investigate further?
Power BI Dashboard Examples: A manufacturing client needed operational dashboards for plant managers. Instead of cramming 15 metrics onto one page—a mistake I see constantly—we created role-specific Power BI dashboard design views. Production managers saw throughput and quality metrics prominently, while maintenance teams focused on equipment health indicators in their Power BI layout. The result? Plant managers actually started using the data to make decisions instead of printing Excel reports.
2. Engineer Visual Hierarchy Using Gestalt Principles
Visual hierarchy in Power BI dashboard design isn’t about making things “look nice”—it’s about directing cognitive resources efficiently. Through A/B testing different Power BI layouts with client teams, I’ve identified specific Power BI design principles that consistently improve comprehension speed.
The 3-Second Rule for Power BI Visualization
Your CEO doesn’t have time to decode your dashboard. If they can’t understand your Power BI dashboard examples’ primary message within 3 seconds, you’ve lost them. I learned this the hard way when a client’s board meeting turned into a 20-minute explanation of what should have been obvious at first glance.
- Size Hierarchy: Most important metrics get 40% larger fonts than secondary data
- Color Emphasis: Use your brand’s primary color for key insights only—I limit this to 2-3 elements maximum in any Power BI layout
- Whitespace Management: Group related Power BI visualization with consistent spacing (I use 8-pixel increments)
Grid-Based Power BI Layout Strategy
Every effective Power BI dashboard design follows an invisible grid. I use a 12-column system that ensures visual alignment across different screen sizes:
- Mobile: Single column stack for Power BI dashboard examples
- Tablet: 6-6 or 4-4-4 splits for Power BI design
- Desktop: 3-3-3-3 or 4-8 combinations for optimal Power BI layout
Power BI Visualization Examples: For a SaaS client’s executive dashboard, we placed their most critical metric (Monthly Recurring Revenue) in a large card visual occupying 4 grid columns, with supporting metrics (churn rate, new signups) in smaller 2-column cards below—a perfect example of how to build a Power BI dashboard that guides attention.
3. Implement Strategic Data Storytelling Frameworks
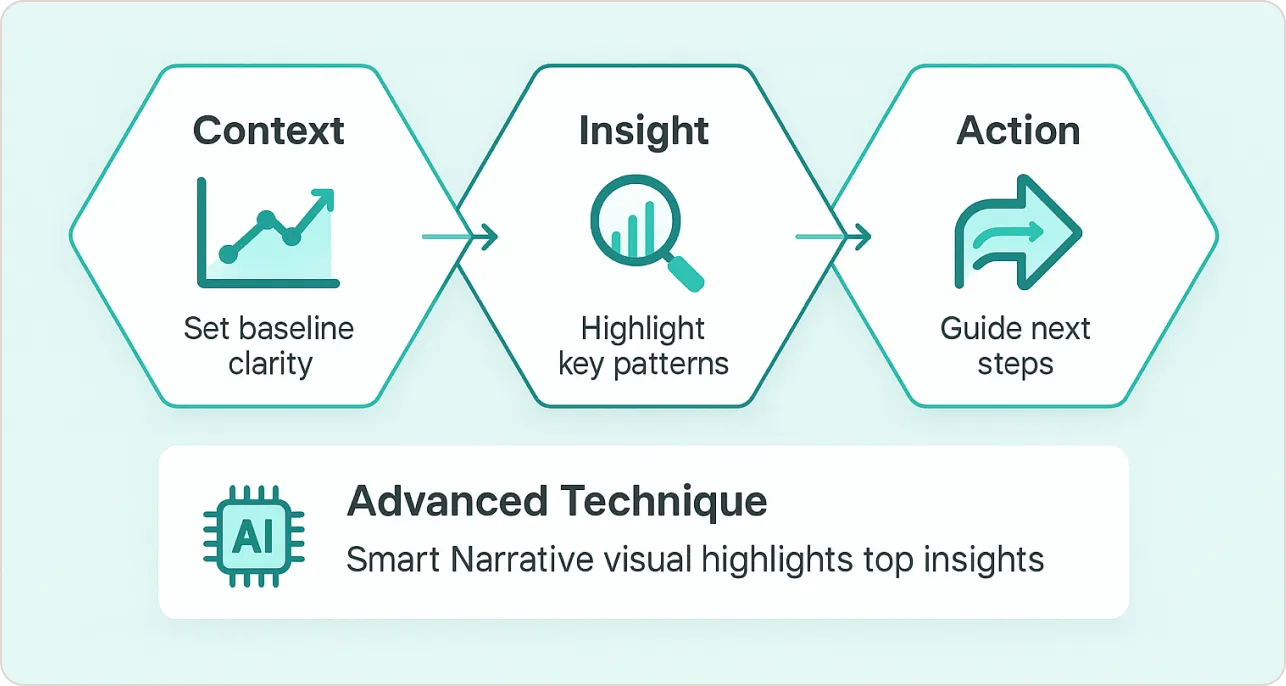
Most Power BI dashboard examples present data—but the best Power BI dashboard design tells stories. After analyzing hundreds of successful implementations, I’ve developed the “Context→Insight→Action” (CIA) framework for how to build a Power BI dashboard that drives decisions.
The CIA Framework for Power BI Design
Context Setting: Establish baseline understanding in your Power BI layout
- Historical trends (3-6 months minimum)
- Industry benchmarks where relevant
- Clear labeling of time periods and data sources
Insight Highlighting: Make patterns obvious in Power BI visualization
- Use conditional formatting to emphasize variance
- Include smart narrative visuals for AI-generated explanations
- Provide variance indicators (+/- from goals)
Action Orientation: Guide next steps through Power BI dashboard design
- Include drill-through capabilities for investigation
- Add bookmarks for common scenarios
- Embed links to relevant tools or processes
Advanced Power BI Dashboard Examples Technique
I integrate Power BI’s Smart Narrative visual in every Power BI dashboard design, but with a specific configuration:
- Position it in the bottom-right quadrant of your Power BI layout
- Configure it to highlight top 2 insights automatically
- Use DAX measures to feed it contextual variance data
Real-World Power BI Dashboard Examples: A retail client’s inventory dashboard uses this Power BI design approach—the smart narrative automatically explains why certain categories are trending up or down, reducing the time managers spend interpreting the Power BI visualization by 60%.
4. Optimize Chart Selection for Cognitive Processing
Chart choice in Power BI dashboard design isn’t about what looks cool—it’s about what your brain can actually process quickly. I used to think pie charts were fine until I watched a CFO spend two minutes trying to figure out which slice was bigger. Now I stick to what actually works.
My Chart Selection Matrix for Power BI Dashboard Examples
Here’s what I’ve learned from watching real people use real Power BI dashboard examples:
Time Series Data: Line charts always work best in Power BI visualization, with these modifications:
- Limit to 5 series maximum in your Power BI layout
- Use direct labeling instead of legends when possible
- Include trend lines for forecasting in Power BI dashboard design
Comparison Data: Horizontal bar charts outperform vertical in 80% of Power BI dashboard examples
- Easier to read category labels in Power BI design
- Natural left-to-right reading pattern for Power BI layout
- Better mobile responsiveness for Power BI dashboard design
Part-to-Whole: Avoid pie charts entirely in Power BI visualization—use horizontal stacked bars or treemaps
- Pie charts require angular comparison (difficult)
- Stacked bars enable linear comparison (intuitive) in Power BI dashboard examples
This aligns with Microsoft’s official Power BI visualization guidelines, which emphasize choosing visuals based on cognitive processing patterns rather than aesthetic preferences.
Power BI Chart Selection
| Chart Type | When to Use | When to Avoid | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Bar Chart | Comparing categories, long labels, rankings | Time series data, continuous trends | Linear comparison (intuitive), easy label reading |
| Line Chart | Time trends, continuous data, forecasting | Categorical comparisons, part-to-whole | Natural left-to-right processing, trend recognition |
| Stacked Bar | Part-to-whole relationships, category breakdowns | More than 6 categories, precise values | Linear vs angular comparison (easier) |
| KPI Cards | Key metrics, executive dashboards, alerts | Detailed breakdowns, comparisons | Instant cognitive recognition, 3-second rule |
| Treemap | Hierarchical data, large datasets, proportions | Precise value comparison, trends | Good for relative sizing, space efficient |
| Scatter Plot | Correlation analysis, outlier detection | Single metric focus, executive summaries | Shows relationships, but requires analytics literacy |
| Pie Chart | NEVER USE | Always avoid in business dashboards | Angular comparison is cognitively difficult |
Advanced Power BI Visualization Strategies
I’ve developed custom visual combinations for Power BI dashboard design that consistently outperform standard approaches:
- The “Spotlight Pattern”: Combine a large KPI card with a small sparkline in your Power BI layout
- The “Context Stack”: Layer current period, prior period, and target as separate measures in Power BI design
- The “Variance Highlight”: Use conditional formatting to emphasize performance gaps in Power BI dashboard examples
5. Master Color Psychology and Accessibility
Color choices in Power BI dashboard design carry semantic meaning that affects user behavior. My approach to Power BI design combines brand consistency with psychological principles when learning how to build a Power BI dashboard.
Strategic Color Implementation in Power BI Layout
- Primary Brand Color: Reserve for the most important metric only in Power BI dashboard examples
- Secondary Colors: Use for categorical distinctions (maximum 6 colors) in Power BI visualization
- Neutral Palette: Gray scale for supporting information in Power BI dashboard design
- Alert Colors: Red for negative variance, green for positive (but test for colorblind accessibility)
Power BI Design Theme Development
I create custom Power BI design themes for every client, but here’s the thing—most organizations already have brand guidelines sitting in a folder somewhere. Instead of reinventing the wheel, I extract the exact hex codes from their existing materials and build themes that actually match their corporate identity.
The key is understanding that Power BI themes aren’t just about colors—they control the entire visual experience. I focus on three core elements:
- Brand Color Hierarchy: Primary color for key metrics, secondary for categories, neutrals for supporting data
- Compliance: Every theme I build passes WCAG 2.1 standards for colorblind users
- Psychological Impact: Colors trigger emotional responses—I use this strategically to guide attention
Accessibility Considerations for Power BI Dashboard Examples
Every Power BI dashboard design I deliver passes WCAG 2.1 AA standards:
- 4.5:1 color contrast ratio minimum
- Alternative text for all visuals
- Keyboard navigation support
- Screen reader compatibility
Following WebAIM’s accessibility guidelines ensures Power BI dashboard examples remain usable for users with visual impairments and meets enterprise compliance requirements.
6. Engineer Performance for Scale
If your Power BI dashboard takes 30 seconds to load, your team will abandon it—no matter how beautiful it looks. I’ve watched executives close perfectly designed Power BI dashboard examples simply because they couldn’t wait for the data to appear. Through extensive performance testing, I’ve identified the critical Power BI visualization optimization techniques that actually work in the real world.
Data Model Optimization for Power BI Design
- Measure Strategy: I write DAX measures for all calculations rather than using implicit measures in Power BI dashboard design
- Data Types: Convert text fields to integers wherever possible (reduces model size by 30-50%)
- Relationship Management: Use bidirectional filtering sparingly—it kills Power BI layout performance
Visual Optimization Techniques for Power BI Dashboard Examples
- Visual Limits: Maximum 6-8 visuals per page (cognitive and performance limit)
- Slicer Strategy: Limit to 3 slicers maximum per page in your Power BI dashboard design
- Custom Visual Caution: Stick to native Power BI visuals when possible
Research from Harvard Business Review on data visualization confirms that cognitive overload occurs when users face too many visual elements simultaneously.
Advanced Performance Hacks for Power BI Visualization
- Aggregation Tables: Pre-calculate common groupings at the data source for Power BI dashboard examples
- Incremental Refresh: Configure for datasets over 1GB in Power BI design
- Composite Models: Separate real-time from historical data in your Power BI layout
Real-World Impact: A financial services client’s executive Power BI dashboard design was taking 45 seconds to load. Their CEO literally said, “This is faster than making coffee, but I don’t have time for either.” After implementing these optimizations, load time dropped to 4 seconds—and executive adoption increased by 300%.
Why Power BI Dashboard Examples Outperform Excel
I’ve rescued dozens of organizations from Excel dashboard hell. Here’s why Excel “dashboards” fail:
- No real-time data: Your numbers are always outdated
- Version control nightmare: Everyone has a different “latest” version
- Security gaps: Sensitive data gets emailed around freely
- Performance breaks: Try refreshing 50MB Excel files with pivot tables
- No mobile access: Good luck reading spreadsheets on phones
Power BI dashboard design solves all these problems while keeping the familiar Microsoft feel that Excel users already understand.
7. Establish Governance and Testing Protocols
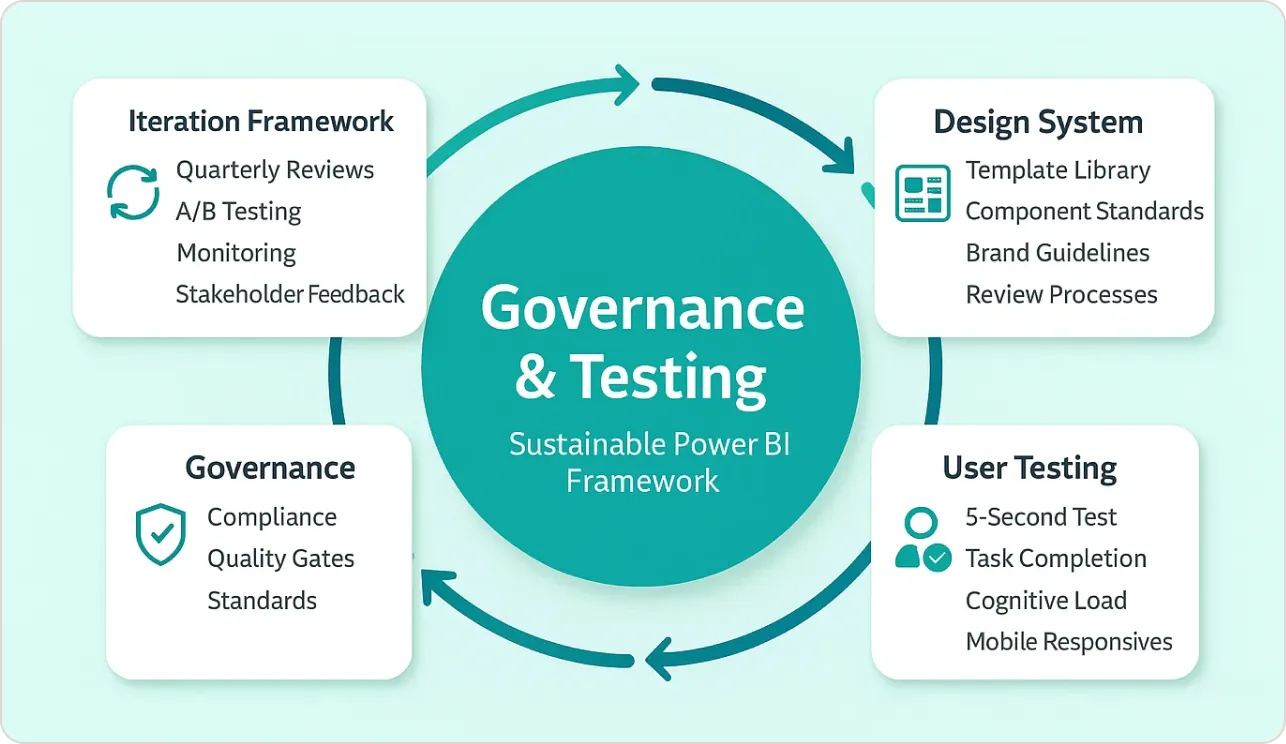
Sustainable Power BI dashboard design requires systematic governance. I’ve developed frameworks that scale from small teams to enterprise deployments using proven Power BI design methodologies.
Design System Implementation for Power BI Dashboard Examples
- Template Library: Standardized Power BI layouts for common scenarios
- Component Standards: Reusable Power BI visualization configurations
- Brand Guidelines: Specific color codes, fonts, and spacing rules for Power BI design
- Review Processes: Quality gates before production deployment
User Testing Methodology for Power BI Dashboard Design
I conduct structured testing for every Power BI dashboard examples:
- 5-Second Test: Can users identify the primary insight?
- Task Completion: Can they find specific information within 30 seconds?
- Cognitive Load Assessment: Do they feel overwhelmed or confident?
- Mobile Responsiveness: Does it work on their actual devices?
These testing protocols align with established usability testing methodologies for enterprise software, ensuring Power BI dashboard examples meet real-world usage patterns rather than theoretical assumptions.
Iteration Framework for Power BI Visualization
- Quarterly Reviews: Assess usage analytics and user feedback for Power BI dashboard design
- A/B Testing: Compare design alternatives with real users using different Power BI layouts
- Performance Monitoring: Track load times and error rates in Power BI dashboard examples
- Stakeholder Interviews: Validate business value delivery through effective Power BI design
10 Best Power BI Dashboard Examples in 2025
Explore 10 best Power BI dashboard examples in 2025 with proven design tips. Learn how to boost performance, improve usability, and deliver faster insights with dashboards that impress executives and drive smarter decisions.
Bonus Hacks: Advanced Power BI Design Techniques
After years of pushing Power BI’s boundaries, I’ve discovered advanced Power BI dashboard design techniques that most consultants don’t know about.
Bookmarked Storytelling in Power BI Design
Create guided analysis paths using Power BI bookmarks for better Power BI dashboard examples:
- Bookmark 1: Overview state in your Power BI layout
- Bookmark 2: Problem identification through Power BI visualization
- Bookmark 3: Root cause analysis using Power BI design
- Bookmark 4: Solution recommendations
Custom Visual Combinations for Power BI Dashboard Design
- The “Executive Summary” Pattern: Combine a large metric card with a mini trending chart in Power BI layout
- The “Exception Report” Layout: Use conditional formatting to highlight only outliers in Power BI dashboard examples
- The “Drill-Through Navigation”: Create hidden detail pages accessible via right-click in Power BI design
AI Integration Strategies for Power BI Visualization
- Smart Narrative Configuration: Train it with custom business context for Power BI dashboard examples
- Copilot Integration: Use natural language queries for ad-hoc analysis in Power BI design
- Automated Insights: Configure key influencers visuals for root cause analysis
Microsoft’s Power BI AI features documentation enable these advanced features, making Power BI dashboard examples more accessible to non-technical users while improving overall Power BI dashboard design effectiveness.
Conclusion: Building Power BI Dashboards That Drive Decisions
Your Power BI dashboard design success isn’t measured by how impressive it looks—it’s measured by how effectively it changes business outcomes. The frameworks in this guide represent thousands of hours of real-world testing across organizations of all sizes.
Focus on three fundamentals: design for your audience’s cognitive patterns, optimize for performance, and test with real users. Whether you’re implementing these strategies internally or seeking expert guidance through Power BI consulting services, remember—design for decisions, not decoration.














